OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
MACD Crossover
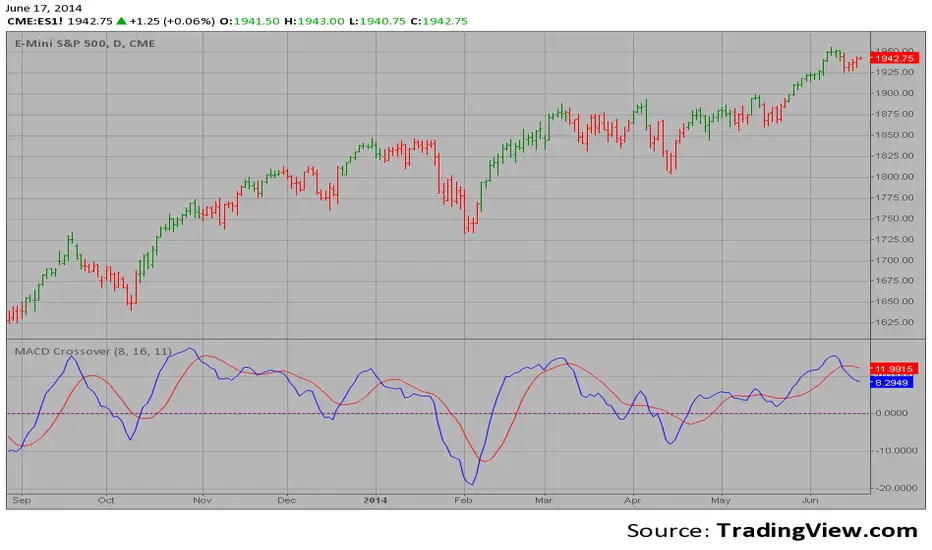
MACD – Moving Average Convergence Divergence. The MACD is calculated
by subtracting a 26-day moving average of a security's price from a
12-day moving average of its price. The result is an indicator that
oscillates above and below zero. When the MACD is above zero, it means
the 12-day moving average is higher than the 26-day moving average.
This is bullish as it shows that current expectations (i.e., the 12-day
moving average) are more bullish than previous expectations (i.e., the
26-day average). This implies a bullish, or upward, shift in the supply/demand
lines. When the MACD falls below zero, it means that the 12-day moving average
is less than the 26-day moving average, implying a bearish shift in the
supply/demand lines.
A 9-day moving average of the MACD (not of the security's price) is usually
plotted on top of the MACD indicator. This line is referred to as the "signal"
line. The signal line anticipates the convergence of the two moving averages
(i.e., the movement of the MACD toward the zero line).
Let's consider the rational behind this technique. The MACD is the difference
between two moving averages of price. When the shorter-term moving average rises
above the longer-term moving average (i.e., the MACD rises above zero), it means
that investor expectations are becoming more bullish (i.e., there has been an
upward shift in the supply/demand lines). By plotting a 9-day moving average of
the MACD, we can see the changing of expectations (i.e., the shifting of the
supply/demand lines) as they occur.
by subtracting a 26-day moving average of a security's price from a
12-day moving average of its price. The result is an indicator that
oscillates above and below zero. When the MACD is above zero, it means
the 12-day moving average is higher than the 26-day moving average.
This is bullish as it shows that current expectations (i.e., the 12-day
moving average) are more bullish than previous expectations (i.e., the
26-day average). This implies a bullish, or upward, shift in the supply/demand
lines. When the MACD falls below zero, it means that the 12-day moving average
is less than the 26-day moving average, implying a bearish shift in the
supply/demand lines.
A 9-day moving average of the MACD (not of the security's price) is usually
plotted on top of the MACD indicator. This line is referred to as the "signal"
line. The signal line anticipates the convergence of the two moving averages
(i.e., the movement of the MACD toward the zero line).
Let's consider the rational behind this technique. The MACD is the difference
between two moving averages of price. When the shorter-term moving average rises
above the longer-term moving average (i.e., the MACD rises above zero), it means
that investor expectations are becoming more bullish (i.e., there has been an
upward shift in the supply/demand lines). By plotting a 9-day moving average of
the MACD, we can see the changing of expectations (i.e., the shifting of the
supply/demand lines) as they occur.
סקריפט קוד פתוח
ברוח האמיתית של TradingView, יוצר הסקריפט הזה הפך אותו לקוד פתוח, כך שסוחרים יוכלו לעיין בו ולאמת את פעולתו. כל הכבוד למחבר! אמנם ניתן להשתמש בו בחינם, אך זכור כי פרסום חוזר של הקוד כפוף ל־כללי הבית שלנו.
כתב ויתור
המידע והפרסומים אינם מיועדים להיות, ואינם מהווים, ייעוץ או המלצה פיננסית, השקעתית, מסחרית או מכל סוג אחר המסופקת או מאושרת על ידי TradingView. קרא עוד ב־תנאי השימוש.
סקריפט קוד פתוח
ברוח האמיתית של TradingView, יוצר הסקריפט הזה הפך אותו לקוד פתוח, כך שסוחרים יוכלו לעיין בו ולאמת את פעולתו. כל הכבוד למחבר! אמנם ניתן להשתמש בו בחינם, אך זכור כי פרסום חוזר של הקוד כפוף ל־כללי הבית שלנו.
כתב ויתור
המידע והפרסומים אינם מיועדים להיות, ואינם מהווים, ייעוץ או המלצה פיננסית, השקעתית, מסחרית או מכל סוג אחר המסופקת או מאושרת על ידי TradingView. קרא עוד ב־תנאי השימוש.