OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Executive Stock Options [Loxx]
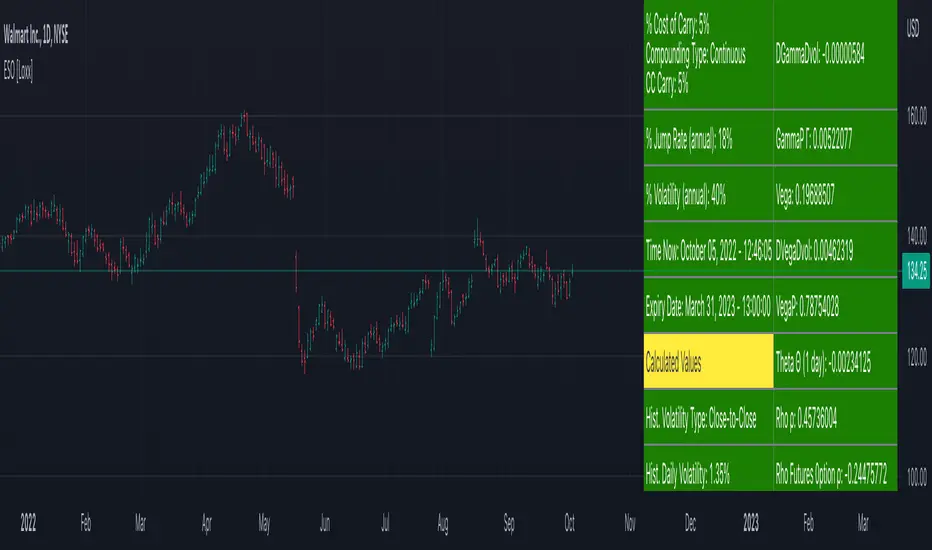
The Jennergren and Naslund (1993) formula takes into account that an employee or executive often loses her options if she has to leave the company before the option's expiration: (via "The Complete Guide to Option Pricing Formulas")
c = e^(-lambda*T) * (Se^((b-r)T) * N(d1) - Xe^-rT * N(d2))
p = e^(-lambda*T) * (Xe^(-rT) * N(-d2) - Se^(b-r)T * N(-d1))
where
d1 = (log(S/X) + (b + v^2/2)T) / vT^0.5
d2 = d1 - vT^0.5
lambda is the jump rate per year. The value of the executive option equals the ordinary Black-Scholes option price multiplied by the probability e —AT that the executive will stay with the firm until the option expires.
b=r options on non-dividend paying stock
b=r-q options on stock or index paying a dividend yield of q
b=0 options on futures
b=r-rf currency options (where rf is the rate in the second currency)
Inputs
S = Stock price.
K = Strike price of option.
T = Time to expiration in years.
r = Risk-free rate
c = Cost of Carry
V = Variance of the underlying asset price
lambda = Jump rate per year
cnd1(x) = Cumulative Normal Distribution
nd(x) = Standard Normal Density Function
convertingToCCRate(r, cmp ) = Rate compounder
Numerical Greeks or Greeks by Finite Difference
Analytical Greeks are the standard approach to estimating Delta, Gamma etc... That is what we typically use when we can derive from closed form solutions. Normally, these are well-defined and available in text books. Previously, we relied on closed form solutions for the call or put formulae differentiated with respect to the Black Scholes parameters. When Greeks formulae are difficult to develop or tease out, we can alternatively employ numerical Greeks - sometimes referred to finite difference approximations. A key advantage of numerical Greeks relates to their estimation independent of deriving mathematical Greeks. This could be important when we examine American options where there may not technically exist an exact closed form solution that is straightforward to work with. (via VinegarHill FinanceLabs)
Things to know
Only works on the daily timeframe and for the current source price.
You can adjust the text size to fit the screen
c = e^(-lambda*T) * (Se^((b-r)T) * N(d1) - Xe^-rT * N(d2))
p = e^(-lambda*T) * (Xe^(-rT) * N(-d2) - Se^(b-r)T * N(-d1))
where
d1 = (log(S/X) + (b + v^2/2)T) / vT^0.5
d2 = d1 - vT^0.5
lambda is the jump rate per year. The value of the executive option equals the ordinary Black-Scholes option price multiplied by the probability e —AT that the executive will stay with the firm until the option expires.
b=r options on non-dividend paying stock
b=r-q options on stock or index paying a dividend yield of q
b=0 options on futures
b=r-rf currency options (where rf is the rate in the second currency)
Inputs
S = Stock price.
K = Strike price of option.
T = Time to expiration in years.
r = Risk-free rate
c = Cost of Carry
V = Variance of the underlying asset price
lambda = Jump rate per year
cnd1(x) = Cumulative Normal Distribution
nd(x) = Standard Normal Density Function
convertingToCCRate(r, cmp ) = Rate compounder
Numerical Greeks or Greeks by Finite Difference
Analytical Greeks are the standard approach to estimating Delta, Gamma etc... That is what we typically use when we can derive from closed form solutions. Normally, these are well-defined and available in text books. Previously, we relied on closed form solutions for the call or put formulae differentiated with respect to the Black Scholes parameters. When Greeks formulae are difficult to develop or tease out, we can alternatively employ numerical Greeks - sometimes referred to finite difference approximations. A key advantage of numerical Greeks relates to their estimation independent of deriving mathematical Greeks. This could be important when we examine American options where there may not technically exist an exact closed form solution that is straightforward to work with. (via VinegarHill FinanceLabs)
Things to know
Only works on the daily timeframe and for the current source price.
You can adjust the text size to fit the screen
הערות שחרור
Corrected static time.הערות שחרור
Corrected UI error. Also, v is volatility not variance in the description above. סקריפט קוד פתוח
ברוח האמיתית של TradingView, יוצר הסקריפט הזה הפך אותו לקוד פתוח, כך שסוחרים יוכלו לעיין בו ולאמת את פעולתו. כל הכבוד למחבר! אמנם ניתן להשתמש בו בחינם, אך זכור כי פרסום חוזר של הקוד כפוף ל־כללי הבית שלנו.
Public Telegram Group, t.me/algxtrading_public
VIP Membership Info: patreon.com/algxtrading/membership
VIP Membership Info: patreon.com/algxtrading/membership
כתב ויתור
המידע והפרסומים אינם מיועדים להיות, ואינם מהווים, ייעוץ או המלצה פיננסית, השקעתית, מסחרית או מכל סוג אחר המסופקת או מאושרת על ידי TradingView. קרא עוד ב־תנאי השימוש.
סקריפט קוד פתוח
ברוח האמיתית של TradingView, יוצר הסקריפט הזה הפך אותו לקוד פתוח, כך שסוחרים יוכלו לעיין בו ולאמת את פעולתו. כל הכבוד למחבר! אמנם ניתן להשתמש בו בחינם, אך זכור כי פרסום חוזר של הקוד כפוף ל־כללי הבית שלנו.
Public Telegram Group, t.me/algxtrading_public
VIP Membership Info: patreon.com/algxtrading/membership
VIP Membership Info: patreon.com/algxtrading/membership
כתב ויתור
המידע והפרסומים אינם מיועדים להיות, ואינם מהווים, ייעוץ או המלצה פיננסית, השקעתית, מסחרית או מכל סוג אחר המסופקת או מאושרת על ידי TradingView. קרא עוד ב־תנאי השימוש.